Metandem, a free and online software for MS-based isobaric labeling metabolomics
Hao et al. (2019) recently published a paper in Analytica Chimica Acta detailing the utility of Metandem, a data analysis software which is aids in isobaric labeling-based metabolomics.
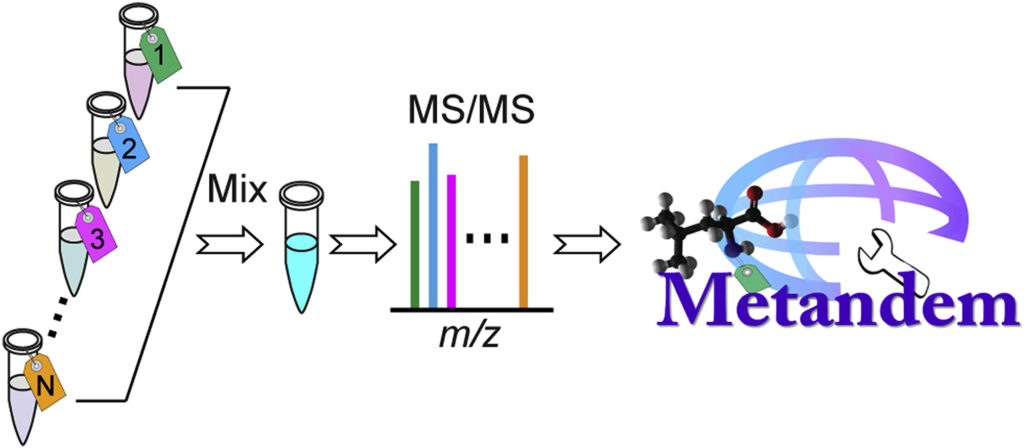
While mass spectrometry-based stable isotope labeling is advantageous compared to other methods of isotope labeling due to its multiplexing and accurate quantification capabilities, its data analysis requires specifically customized bioinformatic tools. However, Metandem, a free, unique and online software, can aid in the analysis of stable isotope labeling-based metabolomics data.
Metandem has a number of different features that assist in MS-based isobaric labeling, such as integrating feature extraction, metabolite quantification and identification, batch processing of multiple data files, online parameter optimization for custom datasets, data normalization and statistical analysis.
Metatandem is available free and online at http://metandem.com/web/.