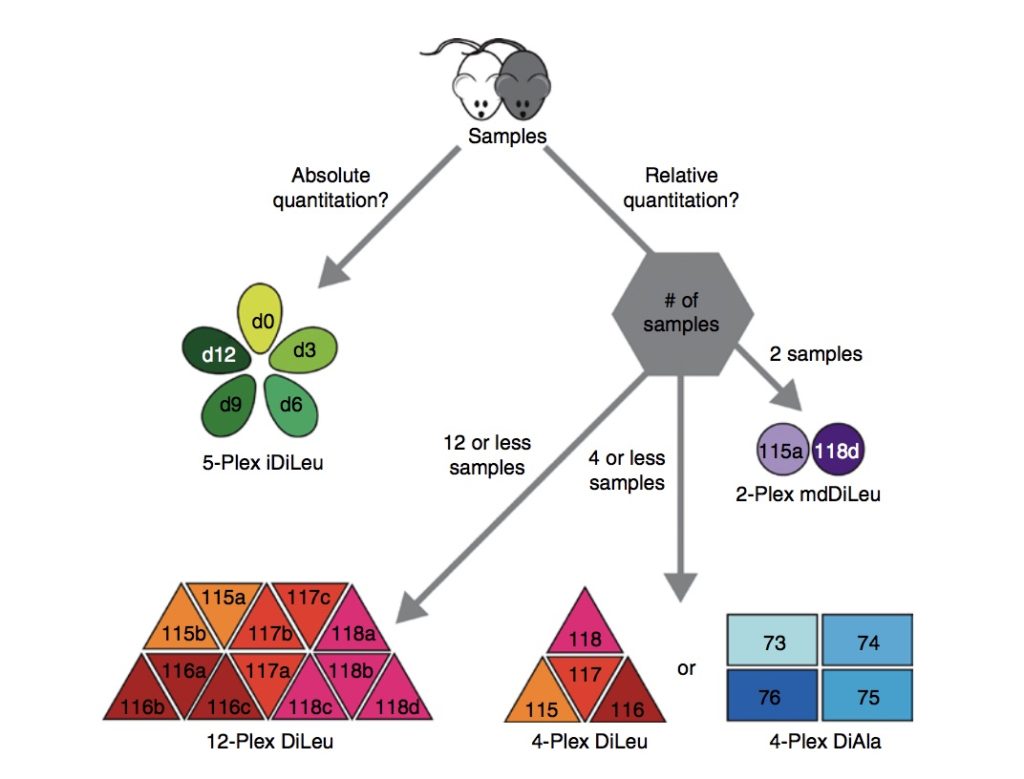
Chemical labeling for glycan and glycopeptide quantitation
Growing implications of glycosylation in human disease have prompted intensive focus on revealing glycomic perturbations through absolute and relative quantification. Empowered by an increasing capacity for detection, identification, and characterization, the past decade has provided a significant increase in the number of suitable strategies for glycan and glycopeptide quantification. In this review, Delafield and Li present the most recent advances in chemical labeling and associated techniques for glycan and glycopeptide quantification.
Read the article: Recent Advances in Analytical Approaches for Glycan and Glycopeptide Quantitation