Acute-Phase proteins differ in mice with and without prostate inflammation
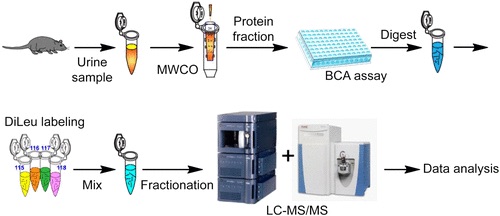
Researchers compared the quantitative proteomic analysis of urine from mice with and without prostate-specific inflammation. Prostate inflammation as it is a key symptom of many different prostate conditions, such as infection and cancer, and therefore by doing so one gains a better understanding of disease mechanisms.
Researchers induced prostate-specific inflammation by conditional prostate epithelial IL-1β expression. Next, they ran urine sample tests and quantified urinary proteins. L. Hao et al found that different levels of acute-phase response proteins (proteins which have plasma concentrations that increase or decrease in response to inflammation) were represented between mice with and without prostate inflammation; these were haptoglobin, inter-α-trypsin inhibitor, and α1-antitrypsin 1-1.
Mass-spectrometry-based quantitative urinary proteomics is an important and powerful method for discovering biomarkers and uncovering molecular urological mechanisms.